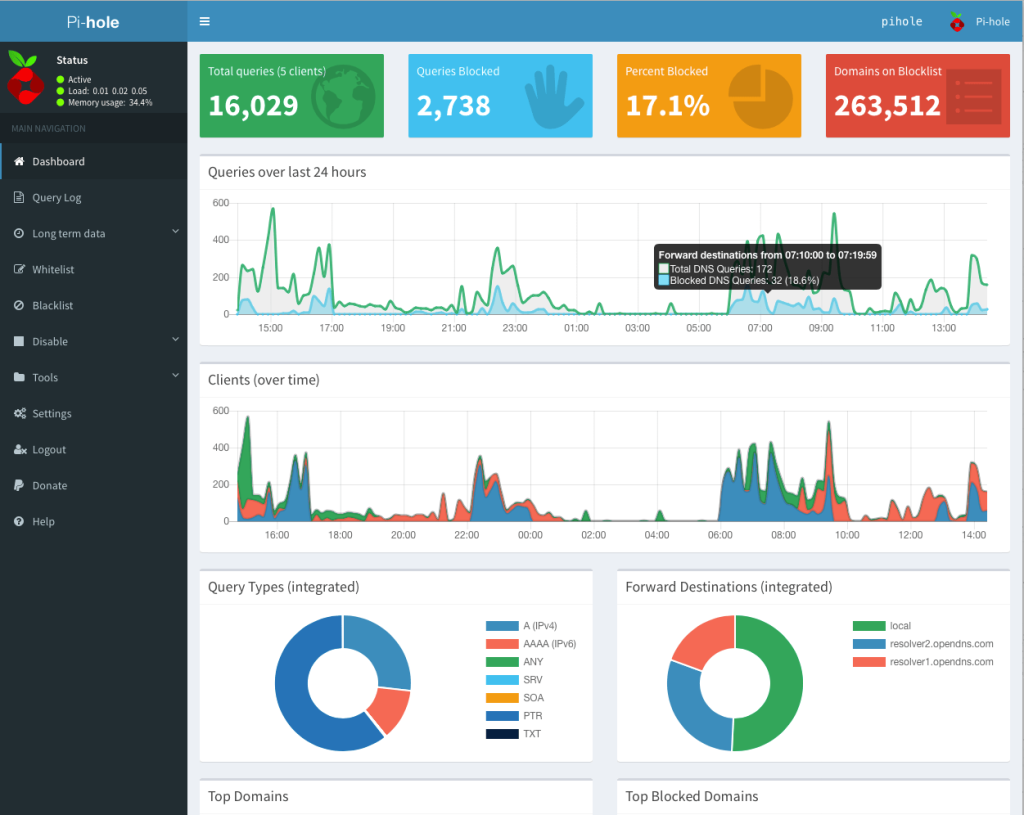
One of the things that bothered me for quite some time with my Pi-Hole was that using it with Google Wifi (first gen), it wouldn’t automatically detect device hostnames. I’d done a lot of googling and never could get it to work even after a lot of different trials with multiple settings.
Eventually I gave up and instead wrote a command that would use nmap to help fill in the gaps, and output to /etc/pihole/custom.list:
#!/bin/bash
if [ "$(id -u)" != "0" ]; then
echo "This script must be run as root" 1>&2
exit 1
fi
echo -n "Looking up MAC and IPs"
for ip in "192.168.1.0" "192.168.2.0" "192.168.3.0"; do
echo -n .
# This is very slow.
nmap -sP "$ip"/20 > "$ip"-nmap.txt
done
echo
# Mega-command to turn the nmap output into a CSV.
cat 192.168.?.0-nmap.txt \
| sed '/^Starting Nmap/ d' \
| sed '/^Host is up/ d' \
| sed '/^Stats:/ d' \
| sed '/^Ping Scan Timing:/ d' \
| sed '/^Nmap done:/ d' \
| sed -z 's/\nMAC/,MAC/g' \
| sed -e 's/Nmap scan report for //g' \
| sed -e 's/MAC Address: //g' \
| sed -e 's/ (/,(/g' \
| grep -Ev $'^[0-9.]+$' \
| sort -u > ip-mac-mapping.csv
rm /etc/pihole/custom.list 2> /dev/null
while IFS=, read -r col1 col2 col3
do
# Strip out opening and closing parenthesis.
col3="${col3//[\(\)]/}"
# Replace all non-alphanumeric characters with dashes.
col3="${col3//[^[:alnum:]]/-}"
# Manually name some of the MACs I already know.
case "$col2" in
"24:05:88:XX:XX:XX")
col3="Google-Wifi"
;;
"B0:19:C6:XX:XX:XX")
col3="Derricks-iPhone"
;;
"CC:44:63:XX:XX:XX")
col3="iPad-Pro"
;;
"C8:D0:83:XX:XX:XX")
col3="Apple-TV-Den"
;;
"50:32:37:XX:XX:XX")
col3="Apple-TV-Bedroom"
;;
"DC:A6:32:XX:XX:XX")
col3="Ubuntu-Server"
;;
"38:F9:D3:XX:XX:XX")
col3="Derrick-MBP"
;;
*)
echo -n
;;
esac
# For some reason, this one is still funky, so I'm adding in a special case for it.
# Could have just been weird caching during my testing.
case "$col1" in
"192.168.1.1")
col3="Google-Wifi"
;;
*)
echo -n
;;
esac
# The PiHole custom.list is supposed to follow the hosts standard, but it seems that
# it is not happy with tabs and comments :sadpanda:
echo "$col1 $col3 # $col2"
echo "$col1 $col3" >> /etc/pihole/custom.list
done < ip-mac-mapping.csvCode language: PHP (php)This will attempt to grab some info about all the devices on your network via nmap, but also allow you to manually override that per IP or per MAC. I have of course stripped out some devices and semi-anonymized my MACs in the above example.
The nmap can be pretty slow, especially if you’re running this on a first gen Raspberry Pi like I am.